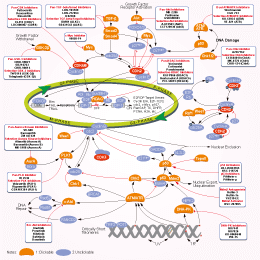
- Bioactive Compounds
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at [email protected] to customize your library.
You could select:
- Antibodies
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-Flag magnetic beads
- Anti-Flag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Magnetic Separator
- Poly DYKDDDDK Tag Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- New Products
- Contact Us
Roscovitine
Synonyms: CYC202, Seliciclib, R-roscovitine
Roscovitine is a potent and selective CDK inhibitor for Cdc2, CDK2 and CDK5 with IC50 of 0.65 μM, 0.7 μM and 0.16 μM in cell-free assays. It shows little effect on CDK4/6. Phase 2.
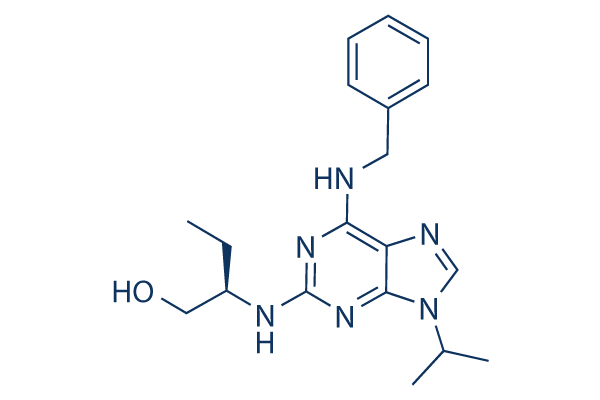
Roscovitine Chemical Structure
CAS No. 186692-46-6
Purity & Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.85%
99.85
Roscovitine Related Products
Signaling Pathway
Cell Data
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LB771-HNC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.9212 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB2241-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.6202 μM | SANGER | |||
| DU-4475 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.4937 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB2518-MEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=47.0448 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H209 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.0115 μM | SANGER | |||
| CGTH-W-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=44.9697 μM | SANGER | |||
| MS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=42.893 μM | SANGER | |||
| GI-ME-N | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=42.6671 μM | SANGER | |||
| DG-75 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=42.6546 μM | SANGER | |||
| MLMA | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=42.2787 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=42.0028 μM | SANGER | |||
| LC-1F | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=41.5705 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1882 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.5998 μM | SANGER | |||
| NTERA-S-cl-D1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=39.5842 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H345 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.9106 μM | SANGER | |||
| MONO-MAC-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.2477 μM | SANGER | |||
| RS4-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.7069 μM | SANGER | |||
| ML-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.6712 μM | SANGER | |||
| OPM-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.2949 μM | SANGER | |||
| LU-139 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.1856 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-684 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.012 μM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.3276 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.3246 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-441-T | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.1148 μM | SANGER | |||
| IMR-5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.3139 μM | SANGER | |||
| K5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.0861 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=34.9422 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2141 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=34.6533 μM | SANGER | |||
| KGN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=34.2524 μM | SANGER | |||
| LP-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.8908 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H64 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.8597 μM | SANGER | |||
| RKO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.5969 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H526 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.4936 μM | SANGER | |||
| GOTO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.9129 μM | SANGER | |||
| Calu-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.4745 μM | SANGER | |||
| LOUCY | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.1253 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-N-FI | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=31.7535 μM | SANGER | |||
| SIG-M5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=31.6833 μM | SANGER | |||
| NKM-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=31.1397 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-SNU-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=31.1059 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H82 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=31.0135 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H510A | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30.0329 μM | SANGER | |||
| ES3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.9582 μM | SANGER | |||
| BB30-HNC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.9483 μM | SANGER | |||
| KM12 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.6239 μM | SANGER | |||
| GI-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.0113 μM | SANGER | |||
| NOS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.9733 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-8 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.908 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-9 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.7969 μM | SANGER | |||
| HL-60 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.9869 μM | SANGER | |||
| QIMR-WIL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.9144 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-299 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=26.8646 μM | SANGER | |||
| KURAMOCHI | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=26.8082 μM | SANGER | |||
| BL-41 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.9597 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2126 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.6529 μM | SANGER | |||
| HOP-62 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.4425 μM | SANGER | |||
| IST-SL2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.5343 μM | SANGER | |||
| HH | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.3819 μM | SANGER | |||
| LS-513 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.5179 μM | SANGER | |||
| EB-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.1831 μM | SANGER | |||
| ACN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.3389 μM | SANGER | |||
| NOMO-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.2008 μM | SANGER | |||
| ES8 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.06 μM | SANGER | |||
| CESS | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.8549 μM | SANGER | |||
| BL-70 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.3274 μM | SANGER | |||
| MHH-PREB-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.0356 μM | SANGER | |||
| BC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.1198 μM | SANGER | |||
| LC4-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.8734 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-320-HSR | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.7688 μM | SANGER | |||
| A101D | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.3208 μM | SANGER | |||
| BC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.0305 μM | SANGER | |||
| TGW | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.8124 μM | SANGER | |||
| JAR | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.0152 μM | SANGER | |||
| HD-MY-Z | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.8246 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1304 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.3601 μM | SANGER | |||
| OS-RC-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.8382 μM | SANGER | |||
| OCI-AML2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.6482 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1599 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.5975 μM | SANGER | |||
| SCC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.2956 μM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-6666 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.9121 μM | SANGER | |||
| MEG-01 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.8379 μM | SANGER | |||
| Raji | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.7894 μM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-8402 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.6262 μM | SANGER | |||
| GCIY | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.8613 μM | SANGER | |||
| 697 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.6007 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-247MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.3516 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.3308 μM | SANGER | |||
| COR-L279 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.2907 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB831-BLC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.5624 μM | SANGER | |||
| ST486 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.351 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-UT-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.35 μM | SANGER | |||
| BB65-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.97495 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-422 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.96336 μM | SANGER | |||
| Becker | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.46082 μM | SANGER | |||
| KS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.45785 μM | SANGER | |||
| JiyoyeP-2003 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.50264 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCCIT | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.55482 μM | SANGER | |||
| MRK-nu-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.12969 μM | SANGER | |||
| A3-KAW | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.76116 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 15958589 | |||
| LP-1 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 3 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human LP-1 cells at 30 uM after 3 hrs using TUNEL staining by flow cytometry | 15958589 | |
| LP-1 | Cytotoxicity assay | 20 to 30 uM | 24 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human LP-1 cells assessed as reduction of cell viability at 20 to 30 uM treated for 24 hrs followed by washout measured after total 72 hrs growth period alamar blue assay relative to control | 15958589 | |
| LP-1 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 1.5 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human LP-1 cells assessed as reduction of RNA polymerase 2 phosphoserine 2 level at 30 uM after 1.5 hrs by immunoblotting | 15958589 | |
| LP-1 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 3 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human LP-1 cells assessed as reduction of Mcl-1 protein level at 30 uM after 3 hrs by immunoblotting | 15958589 | |
| LP-1 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 3 to 5 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human LP-1 cells assessed as increase in level of cleaved PARP at 30 uM after 3 to 5 hrs by immunoblotting | 15958589 | |
| NCI-H929 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 5 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human NCI-H929 cells assessed as increase in level of cleaved PARP at 30 uM after 5 hrs by immunoblotting | 15958589 | |
| NCI-H929 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 1.5 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human NCI-H929 cells assessed as fast slow migrating hyperphosphorylated RNA polymerase 2O form at 30 uM after 1.5 hrs by immunoblotting | 15958589 | |
| RPM18226 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 1.5 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human RPM18226 cells assessed as reduction of RNA polymerase 2 phosphoserine 2 level at 30 uM after 1.5 hrs by immunoblotting | 15958589 | |
| RPM18226 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 3 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human RPM18226 cells assessed as reduction of Mcl-1 protein level at 30 uM after 3 hrs by immunoblotting | 15958589 | |
| RPM18226 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 3 to 5 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human RPM18226 cells assessed as increase in level of cleaved PARP at 30 uM after 3 to 5 hrs by immunoblotting | 15958589 | |
| NCI-H929 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 3 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human NCI-H929 cells assessed as changes in XIAP protein level at 30 uM after 3 hrs by immunoblotting | 15958589 | |
| NCI-H929 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 3 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human NCI-H929 cells assessed as changes in survivin protein level at 30 uM after 3 hrs by immunoblotting | 15958589 | |
| RPM18226 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 3 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human RPM18226 cells at 30 uM after 3 hrs using TUNEL staining by flow cytometry | 15958589 | |
| NCI-H929 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 1.5 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human NCI-H929 cells assessed as reduction of RNA polymerase 2 phosphoserine 2 level at 30 uM after 1.5 hrs by immunoblotting | 15958589 | |
| NCI-H929 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 1.5 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human NCI-H929 cells assessed as dephosphorylation of pRb at S249/T252 at 30 uM after 1.5 hrs by immunoblotting | 15958589 | |
| NCI-H929 | Cytotoxicity assay | 20 to 30 uM | 16 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human NCI-H929 cells assessed as reduction of cell viability at 20 to 30 uM treated for 16 hrs followed by washout measured after total 72 hrs growth period alamar blue assay relative to control | 15958589 | |
| NCI-H929 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 3 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human NCI-H929 cells assessed as reduction of Mcl-1 protein level at 30 uM after 3 hrs by immunoblotting | 15958589 | |
| NCI-H929 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 3 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human NCI-H929 cells assessed as changes in Bcl-2 protein level at 30 uM after 3 hrs by immunoblotting | 15958589 | |
| NCI-H929 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 3 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human NCI-H929 cells at 30 uM after 3 hrs using TUNEL staining by flow cytometry | 15958589 | |
| NCI-H929 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 1.5 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human NCI-H929 cells assessed as reduction of RNA polymerase 2 phosphoserine 5 level at 30 uM after 1.5 hrs by immunoblotting | 15958589 | |
| NCI-H929 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 1.5 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human NCI-H929 cells assessed as reduction of Hdm2 level at 30 uM after 1.5 hrs by immunoblotting | 15958589 | |
| NCI-H929 | Apoptosis assay | 30 uM | 1.5 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human NCI-H929 cells assessed as increase of p53 accumulation at 30 uM after 1.5 hrs by immunoblotting | 15958589 | |
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 21080703 | |||
| HCT116 | Function assay | 30 to 40 umol/L | 24 hrs | Inhibition of cyclin A in human HCT116 cells assessed as decrease in protein level at 30 to 40 umol/L after 24 hrs by immunoblotting analysis | 21080703 | |
| HCT116 | Function assay | 30 to 40 umol/L | 24 hrs | Inhibition of cyclin B in human HCT116 cells assessed as decrease in protein level at 30 to 40 umol/L after 24 hrs by immunoblotting analysis | 21080703 | |
| HCT116 | Function assay | 30 to 40 umol/L | 24 hrs | Inhibition of cyclin D1 in human HCT116 cells assessed as decrease in protein level at 30 to 40 umol/L after 24 hrs by immunoblotting analysis | 21080703 | |
| HCT116 | Function assay | 30 to 40 umol/L | 24 hrs | Inhibition of CDK2 in human HCT116 cells assessed as decrease in protein level at 30 to 40 umol/L after 24 hrs by immunoblotting analysis | 21080703 | |
| HT-29 | Function assay | 2.5 to 40 uM | 24 hrs | Inhibition of retinoblastoma protein in human HT-29 cells assessed as reduction of cyclin A level at 2.5 to 40 uM after 24 hrs by immunoblotting | 21417417 | |
| MCF7 | Cell cycle assay | 24 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human MCF7 cells assessed as accumulation at G2/M phase after 24 hrs using propidium iodide and BrdU staining by flow cytometry | 21417417 | ||
| RPMI8226 | Cell cycle assay | 24 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human RPMI8226 cells assessed as accumulation at G2/M phase after 24 hrs using propidium iodide and BrdU staining by flow cytometry | 21417417 | ||
| MCF7 | Cell cycle assay | 24 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human MCF7 cells assessed as decrease in S phase cell population after 24 hrs using propidium iodide and BrdU staining by flow cytometry | 21417417 | ||
| MCF7 | Cell cycle assay | 24 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human MCF7 cells assessed as accumulation at sub-G1 phase after 24 hrs using propidium iodide and BrdU staining by flow cytometry | 21417417 | ||
| RPMI8226 | Cell cycle assay | 24 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human RPMI8226 cells assessed as accumulation at sub-G1 phase after 24 hrs using propidium iodide and BrdU staining by flow cytometry | 21417417 | ||
| MCF7 | Cell cycle assay | 80 uM | 24 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human MCF7 cells assessed as reduction of actively replicating DNA level at 80 uM after 24 hrs using propidium iodide and BrdU staining by flow cytometry | 21417417 | |
| MCF7 | Function assay | 20 uM | 24 hrs | Induction of p53-dependent transcriptional activity in human MCF7 cells assessed as increase of p21 WAF1 level at 20 uM after 24 hrs by immunofluorescence assay | 21417417 | |
| RPMI8226 | Cell cycle assay | 24 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human RPMI8226 cells assessed as decrease in S phase cell population after 24 hrs using propidium iodide and BrdU staining by flow cytometry | 21417417 | ||
| RPMI8226 | Cell cycle assay | 80 uM | 24 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human RPMI8226 cells assessed as reduction of actively replicating DNA level at 80 uM after 24 hrs using propidium iodide and BrdU staining by flow cytometry | 21417417 | |
| A549 | Apoptosis assay | 2 uM | 48 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human A549 cells assessed as DNA fragmentation at 2 uM after 48 hrs by agarose gel electrophoresis | 23623491 | |
| Sf9 | Function assay | 10 mins | Inhibition of His-6-tagged recombinant human CDK2/cyclinE expressed in baculovirus-infected sf9 cells using histone H1 as substrate after 10 mins by liquid scintillation counting in presence of [gamma-32P]ATP, IC50 = 0.1 μM. | 24417566 | ||
| BJ | Function assay | 10 uM | 10 days | Suppression of senescence in human BJ cells assessed as increase in cell number at 10 uM after 10 days by senescence reversal assay | 24681986 | |
| BJ | Function assay | 10 uM | 10 days | Inhibition of ataxia telangiectasia-mutated in human BJ cells assessed as increase in cell number at 10 uM after 10 days by senescence reversal assay | 24681986 | |
| MCF7 | Function assay | 10 uM | 10 mins | Sensitization of infrared-induced DNA damage in human MCF7 cells assessed as reduction in colony formation at 10 uM pretreated for 10 mins followed by irradiation for 4 hrs measured after 10 days by crystal violet staining analysis | 26851505 | |
| Caco2 | Cell cycle assay | Cell cycle arrest in human Caco2 cells assessed as accumulation at G1/S phase by Hoechst staining based fluorescence assay | 28214231 | |||
| HaCaT | Cell cycle assay | Cell cycle arrest in human HaCaT cells assessed as accumulation at G1/S phase by Hoechst staining based fluorescence assay | 28214231 | |||
| HuH7 | Cell cycle assay | Cell cycle arrest in human HuH7 cells assessed as accumulation at G1/S phase by Hoechst staining based fluorescence assay | 28214231 | |||
| PC3 | Cell cycle assay | Cell cycle arrest in human PC3 cells assessed as accumulation at G2/M phase by Hoechst staining based fluorescence assay | 28214231 | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Cell cycle assay | Cell cycle arrest in human MDA-MB-231 cells assessed as accumulation at G1/S phase by Hoechst staining based fluorescence assay | 28214231 | |||
| HCT116 | Cell cycle assay | Cell cycle arrest in human HCT116 cells assessed as accumulation at G1/S phase by Hoechst staining based fluorescence assay | 28214231 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 28557430 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 30199702 | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Biological Activity
| Description | Roscovitine is a potent and selective CDK inhibitor for Cdc2, CDK2 and CDK5 with IC50 of 0.65 μM, 0.7 μM and 0.16 μM in cell-free assays. It shows little effect on CDK4/6. Phase 2. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
| In vitro | ||||
| In vitro | Roscovitine displays high efficiency and high selectivity towards some cyclin-dependent kinases with IC50 of 0.65, 0.7, 0.7 and 0.16 μM for cdc2/cyclin B, cdk2/cyclin A, cdk2/cyclin E and cdk5/p53, respectively. [1] Roscovitine reversibly inhibits the prophaselmetaphase transition in the micromolar range of starfish oocytes and sea urchin embryos, inhibits in vitro M-phase-promoting factor activity and in vitro DNA synthesis in Xenopus egg extracts, and suppresses the proliferation of mammalian cell lines with an average IC50 of 16 μM. [1] In mesangial cells, Roscovitine results in a dose-dependent reduction of CDK2 activity that at concentrations of 7.5, 12.5 and 25 mM, Roscovitine causes a 25, 50% and 100% decrease in CDK2 activity, respectively. [2] A recent study shows that Roscovitine inhibits cdk5 kinase activity, cell proliferation, multicellular development, and cdk5 nuclear translocation in Dictyostelium discoideum, without affecting the expression of cdk5 protein during axenic growth. [3] |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinase Assay | Enzymes | |||
| Kinases activities are assayed at 30 °C in buffer C. Blank values are subtracted from the data and activities calculated as molar amount of phosphate incorporated in protein acceptor during a 10-minute incubation. Controls are performed with appropriate dilutions of DMSO. In a few cases, phosphorylation of the substrate is assessed by autoradiography after SDS/PAGE. p34cdc2/cyclin B is purified from M-phase starfish (M. glacialis) oocytes by affinity chromatography. It is assayed with 1 mg histone Hl/mL, in the presence of 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP (3000 Ci/mmol; 1 mCi/mL) in a final volume of 30 μL. After a 10-minute incubation at 30 °C, 25-μL aliquots of supernatant are spotted onto pieces of Whatman P81 phosphocellulose paper, and, after 20 seconds, the filters are washed five times (for at least 5 minutes each time) in a solution of 10mL phosphoric acid/L water. The wet filters are transferred into 6-mL plastic scintillation vials, 5 mL ACS scintillation fluid is added and the radioactivity measured in a Packard counter. The kinase activity is expressed as molar amount of phosphate incorporated in histone H1 during a 10-minutes incubation or as a percentage of maximal activity. p33cdk2/cyclin A and p33cdk2/cyclinE are reconstituted from extracts of sf9 insect cells infected with various baculoviruses. Cyclins A and E are fusion proteins with glutathione S-transferase and the complexes are purified on glutathione-agarose beads. Kinase activities are assayed with 1 mg/mL histone H1, in the presence of 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP, during 10 minutes, in a final volume of 30 μL, as described for the p34cdc2/cyclin B kinase. p33cdk5/p35 is purified from bovine brain, excluding the Mono S-chromatographic step. The active fractions from the Superose 12 column are pooled and concentrated to a final concentration of approximately 25 μg enzyme/mL. The kinase is assayed with 1 mg/mL histone HI in the presence of 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP, during 10 minutes in a final volume of 30 μL, as described for the p34cdc2/cyclin B kinase. p33cdk5/cyclin D1 is obtained from insect cell lysates. Cdk4 is a fusion protein with glutathione-S-transferase and the active complex is purified on glutathione-agarose beads. Its kinase activity is assayed with purified retinoblastoma protein (complexed with glutathione-S-transferase) in the presence of 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP, in a final volume of 30 μL. After a 15-minute incubation, 30 μL Laemmli sample buffer is added. The phosphorylated substrate is resolved by 10 % SDS/PAGE and analysed by autoradiography by overnight exposure to Hyperfilm MP and densitometry. p33cdk4/cyclinD 2 is obtained from insect cell lysates. It is assayed with purified retinoblastoma protein (complexed with glutathione-S-transferase) in the presence of 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP in a final volume of 30 μL. After a 30-minute incubation, 30 μL Laemmli sample buffer is added. The phosphorylated substrate is resolved by 10% SDS/PAGE and analysed by autoradiography by overnight exposure to Hyperfilm MP and densitometry. MAP kinase erkl (tagged with glutathione-S-transferase), is expressed in bacteria, purified on glutathione-agarose beads and assayed with 1 mg myelin basic protein/ml in the presence of 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP as described above for the p34cdc2cyclin B kinase. His-tagged erkl and erk2 are activated in vitro by mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, purified (Ni-affinity and Mono Q) and assayed as described above during 10 minutes in a final volume of 30 μL. The catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase, purified from bovine heart, is assayed with 1 mg histone Hl/ml, in the presence of 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP as described for the p34cdc2/cyclin B kinase. cGMP-dependent protein kinase, purified to homogeneity from bovine tracheal smooth muscle, is assayed with 1 mg histone Hl/mL, in the presence of 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP as described for the p34cdc2/cyclin B kinase. Casein kinase 2 is isolated from rat liver cytosol and assayed with 1 mg casein/mL and 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP. The substrate is spotted on Whatmann 3MM filters and washed with 10% (mass/vol.) trichloroacetic acid. Myosin light chain kinase, purified from chicken gizzard is assayed in the presence of 100 nM calmodulin, 100 μM CaCl2, 50 mM Hepes, 5 mM MgCI,, 1 mM dithiothreitol and 0.1 mg BSA/ml at pH 7.5 using a synthetic peptide based on the smooth-muscle myosin light-chain phosphorylation site and in the presence of 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP, in a final volume of 50 μL. Incorporation of radioactive phosphate is monitored on phosphocellulose filters as described above. ASK-γ, a plant homologue of GSK-3, is expressed as a glutathione-S-transferase fusion protein in Escherichia coli and purified on glutathione-agarose. ASK-γ kinase is assayed, for 10 minutes at 30 °C, with 5 μg myelin basic protein, in the presence of 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP in a final volume of 30 μL. The phosphorylated myelin basic protein is recovered on Whatman P81 phosphocellulose paper as described for the p34cdc2/cyclin B kinase. Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase domain (CIRK-41) is overexpressed in a baculovirus system and purified to homogeneity. Its kinase activity is assayed, for 10 minutes at 30 °C, with 5 μg Raytide, in the presence of 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP, in a final volume of 30 μL. The phosphorylated Raytide is recovered on Whatman P81 phosphocellulose paper as described for the p34cdc2/cyclin B kinase. c-src kinase is purified from infected Sf9 cells. The v-abl kinase is expressed in E. coli and affinity purified on IgG Affigel 10. Both kinases are assayed for 10 minutes at 30 °C, with 5 μg Raytide, in the presence of 15 μM [γ-32P]ATP, in a final volume of 30 μL. The phosphorylated Raytide is recovered on Whatman P81 phosphocellulose paper as described for the p34cdc2/cyclin B kinase. | ||||
| Cell Research | Cell lines | Leukemia, non-small cell lung cancer, colon cancer, central nervous system cancer, melanoma, ovarian cancer, renal cancer, prostate cancer, breast cancer | ||
| Concentrations | 0.01 - 100 μM | |||
| Incubation Time | 48 hours | |||
| Method | 60 human tumour cell lines comprising nine tumor types are cultured for 24 hours prior to a 48-hour continuous exposure to 0.01-100 μM roscovitine. A sulforhodaminine B protein assay is used to estimate the cytotoxicity. |
|||
| Experimental Result Images | Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
| Western blot | pT231-tau / pS202-tau / tau p-Rb / p-CDK2 / CDK2 / Cyclin D1 / Cyclin A2 / ERα / ERβ/ AIB1 / PELP1 |
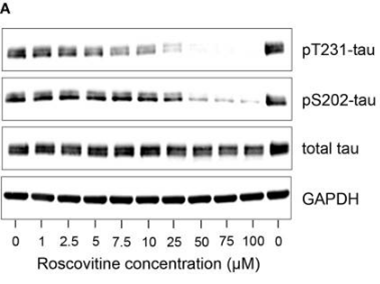
|
30915013 | |
| Immunofluorescence | CDK1 / Smek2 / FUBP1 / Cdc20 E2F1 / FASN / Bmi1 / Cyclin D2 / CDK2 / CDK4 |
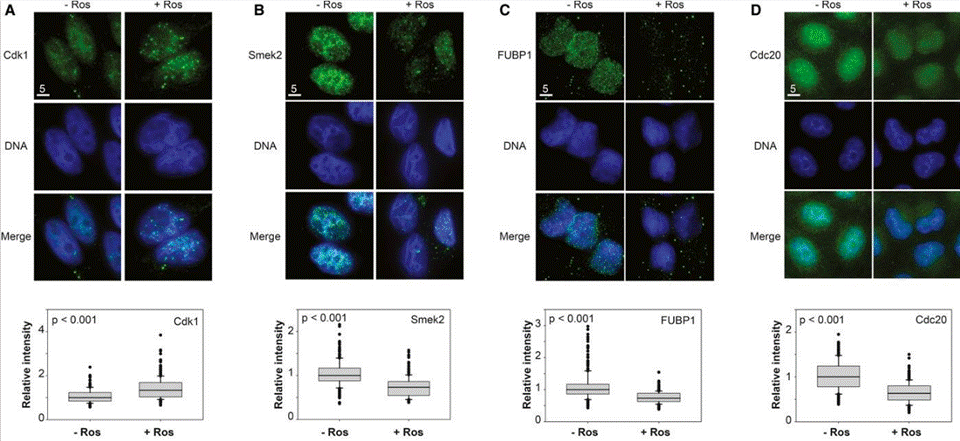
|
24534090 | |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
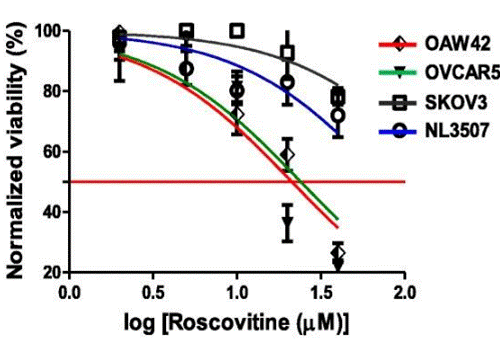
|
29996940 | |
| In Vivo | ||
| In vivo | Roscovitine, at a dose of 50 mg/kg, significantly inhibits growth of The Ewing's sarcoma family of tumors (ESFT) xenografts. [4] Roscovitine enhances the antitumor effect of doxorubicin without increased toxicity with a mechanism that involves cell cycle arrest rather than apoptosis in nude mice bearing established MCF7 xenografts. [5] |
|
|---|---|---|
| Animal Research | Animal Models | A4573 cells are injected s.c. into the right posterior flank of CD1 nu/nu mice. |
| Dosages | ≤50 mg/kg | |
| Administration | Administered via i.p. | |
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02649751 | Terminated | Cystic Fibrosis |
University Hospital Brest|ManRos Therapeutics|Cyclacel Pharmaceuticals Inc. |
February 22 2016 | Phase 2 |
Chemical Information & Solubility
| Molecular Weight | 354.45 | Formula | C19H26N6O |
| CAS No. | 186692-46-6 | SDF | Download Roscovitine SDF |
| Smiles | CCC(CO)NC1=NC(=C2C(=N1)N(C=N2)C(C)C)NCC3=CC=CC=C3 | ||
| Storage (From the date of receipt) | |||
|
In vitro |
DMSO : 71 mg/mL ( (200.31 mM) Moisture-absorbing DMSO reduces solubility. Please use fresh DMSO.) Ethanol : 71 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molecular Weight Calculator |
|
In vivo Add solvents to the product individually and in order. |
In vivo Formulation Calculator |
||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Molarity Calculator
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Tech Support
Answers to questions you may have can be found in the inhibitor handling instructions. Topics include how to prepare stock solutions, how to store inhibitors, and issues that need special attention for cell-based assays and animal experiments.
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
* Indicates a Required Field
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1:
How can I reconstitute the drug for in vivo studies?
Answer:
S1153 in 1% DMSO+10% Tween 80+20% N-N-dimethylacetamide+PEG 400 is a clear solution which is okay for injection. And S1153 in 1% DMSO+30% polyethylene glycol+1% Tween 80 at 30mg/ml is a suspension, which is fine for oral gavage.
Tags: buy Roscovitine | Roscovitine supplier | purchase Roscovitine | Roscovitine cost | Roscovitine manufacturer | order Roscovitine | Roscovitine distributor